コメンタリー
Abdifatah Aden Abdi, "Somalia's Perspective on the Free and Open Indo-Pacific: A Path to Peace and Conflict Resolution" (ROLES Commentary No. 28)
Abstract
The Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) has emerged as a strategic framework to preserve a rules-based order, ensure freedom of navigation, and promote economic prosperity in the Indo-Pacific region. Initially proposed by Japan and endorsed by the United States and other like-minded partners, the FOIP responds to evolving geopolitical dynamics, particularly China's increasing influence and assertiveness in the region. At its core, the FOIP emphasizes respect for international law, transparency, and adherence to democratic norms, with the goal of fostering stability and cooperation among nations in the Indo-Pacific.
In discussions surrounding the FOIP, smaller and less influential nations like Somalia often overlook perspectives integral to the region's security architecture. Somalia's strategic location at the crossroads of the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea, combined with its extensive coastline, bestows upon it significant geopolitical importance. Despite internal challenges such as political instability, armed conflict, and governance deficiencies, Somalia's fate is closely intertwined with broader regional dynamics, making its perspective on the FOIP particularly relevant.
1. Introduction
Somalia is located in the Horn of Africa and plays a significant role in the broader Indo-Pacific region due to its strategic location along critical maritime routes. Despite facing internal challenges such as political instability and terrorism, Somalia's geographical position offers it potential as a vital player in the Indo-Pacific region. In recent years, Somalia has been making efforts to rebuild its state institutions and enhance its regional and international engagements. As part of this process, Somalia has sought to strengthen its ties with countries that share the FOIP vision, including the United States, Japan, India, and other regional powers. In recent years, Somalia has been making efforts to rebuild its state institutions and enhance its regional and international engagements. As part of this process, Somalia has sought to strengthen its ties with countries that share the FOIP vision.
For Somalia, participating in the FOIP initiative offers opportunities for economic development, security cooperation, and diplomatic engagement. Enhancing maritime security in the Indian Ocean, promoting trade and investment, and fostering regional connectivity are key areas where Somalia can contribute to and benefit from the FOIP strategy. Overall, Somalia's engagement in the Free and Open Indo-Pacific reflects its aspirations to leverage its strategic position, enhance regional integration, and promote peace, stability, and prosperity in the broader Indo-Pacific region.
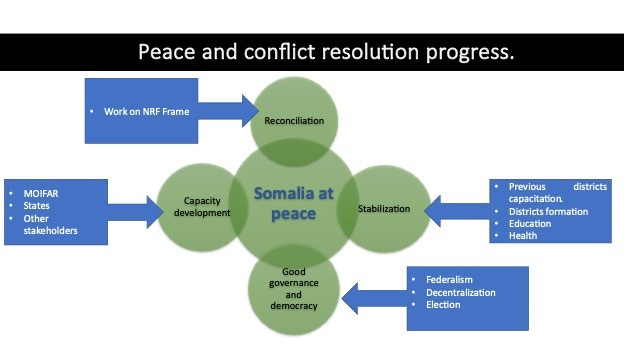
Somalia's strategic location, maritime significance, economic potential, security challenges, and diplomatic engagement make it a potential contributor to the Free and Open Indo-Pacific initiative. By addressing its security concerns, promoting economic development, enhancing regional cooperation, and engaging constructively with international partners, Somalia can play a constructive role in advancing the goals of a free, open, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region. Somalia can contribute to the Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) initiative in several ways:
Maritime Security: Somalia's coastline along the Indian Ocean is strategically important for maritime security in the Indo-Pacific region. However, the country has faced challenges such as piracy and illegal fishing in its waters. By enhancing its maritime law enforcement capabilities and participating in regional maritime security initiatives, Somalia can contribute to safeguarding the freedom of navigation and combatting illicit activities in the Indian Ocean.
Counterterrorism and Stability: Somalia has been grappling with instability and the presence of terrorist groups like Al-Shabaab. Addressing these security concerns is crucial for promoting stability within Somalia and the Indo-Pacific region. Somalia's cooperation with international partners in counterterrorism efforts can contribute to combating extremism and fostering a secure environment conducive to economic development and regional cooperation.
Economic Development: Somalia has untapped economic potential, particularly in sectors such as fisheries, agriculture, and trade. By promoting economic development and investment opportunities, Somalia can contribute to the economic growth and prosperity of the Indo-Pacific region. Enhancing connectivity through infrastructure development and trade facilitation, initiatives can further integrate Somalia into regional economic networks and promote economic openness and cooperation.
Humanitarian Assistance and Capacity Building: Somalia has been affected by recurrent droughts, famine, and humanitarian crises. Somalia can address humanitarian challenges and build resilience in the region by providing humanitarian assistance and engaging in capacity-building efforts. Collaborative initiatives focused on disaster preparedness, healthcare, and education can strengthen Somalia's capacity to respond to emergencies and contribute to the overall stability and well-being of the Indo-Pacific region.
Diplomatic Engagement and Regional Cooperation: Somalia's participation in regional forums and initiatives can foster dialogue, cooperation, and mutual understanding among countries in the Indo-Pacific region. By engaging in multilateral diplomacy and promoting regional cooperation on peacebuilding, counterterrorism, and maritime security, Somalia can contribute to shaping a more inclusive and cooperative regional order that upholds the principles of freedom, openness, and respect for international law.
1.2 Objectives and Structure of the Essay
This essay explores Somalia's perspective on the Free and Open Indo-Pacific, focusing on its implications for peace and conflict resolution in the Horn of Africa. By examining Somalia's historical context, strategic significance, and engagement with the FOIP framework, the essay seeks to elucidate pathways for Somalia to leverage the FOIP for peace-building and regional cooperation. Structurally, the essay will provide a historical overview of Somalia's trajectory, analyze its strategic importance in the Indo-Pacific context, examine the implications of the FOIP for Somalia, delineate pathways for peace and conflict resolution within the FOIP framework, draw on case studies and best practices, and conclude by summarizing key findings and offering recommendations.
2. Historical Context
2.1 Somalia's Colonial Legacy
Somalia's modern history has been significantly shaped by its colonial past, with European powers controlling different parts of the territory. Italy colonized southern Somalia, forming Italian Somaliland, while the northern regions were under British rule, forming British Somaliland. The colonial era left lasting impacts on Somalia's political, social, and economic landscape.
2.2 Post-Independence Struggles
Somalia has had a past with Post-Independence Struggles. In 1960, Somalia gained independence through the unification of Italian and British Somaliland. However, the newly formed Somali Republic faced numerous challenges, including internal divisions, clan rivalries, and economic disparities. Successive governments grappled with governance issues as Somalia sought to forge a cohesive national identity amidst ethnic diversity.
2.3 Civil War and State Collapse
The collapse of the Siad Barre regime in 1991 plunged Somalia into a prolonged civil war characterized by clan-based violence, warlordism, and state fragmentation. The absence of central authority led to a power vacuum, with various factions competing for control. The resulting humanitarian crisis attracted international attention and intervention.
2.4 Emergence of Al-Shabaab
Amidst the chaos of civil war, extremist groups like Al-Shabaab emerged, exploiting the governance vacuum to advance their ideological agenda. Initially a radical offshoot of the Islamic Courts Union, Al-Shabaab grew in strength and influence, posing challenges to efforts aimed at stabilizing Somalia and restoring peace.
2.5 Climate change
Climate change poses multifaceted challenges for Somalia, impacting food security, water availability, livelihoods, and socio-economic stability. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach that integrates climate adaptation measures, sustainable resource management, disaster risk reduction, and community resilience-building initiatives. International cooperation and support are essential to assist Somalia in mitigating the impacts of climate change and building adaptive capacity to ensure a more sustainable and resilient future.
3. Somalia's Strategic Importance
3.1 Geopolitical Significance
Somalia's geopolitical significance stems from its strategic location, a crucial junction between the Indian Ocean and the Red Sea. This positioning establishes Somalia as a pivotal gateway connecting Africa and Asia.
The country's extensive coastline is particularly significant in this context. It provides access to sea lanes that are vital for global trade and commerce. These sea lanes facilitate the movement of goods, energy resources, and people between disparate regions of the world.
Moreover, Somalia's maritime hub status enhances its importance in maritime security matters. Given the increasing concerns over piracy, illegal trafficking, and other maritime threats in the region, Somalia's role in ensuring security along these crucial sea routes becomes indispensable.
Furthermore, Somalia's location also makes it significant in energy transit. The country's proximity to major oil-producing regions in the Middle East and its access to important sea routes make it a potential hub for energy transportation. This adds another layer to Somalia's geopolitical relevance as it becomes involved in global energy dynamics and trade.
3.2 Maritime Security Challenges
Despite its importance, Somalia's maritime domain faces security challenges such as piracy, illegal fishing, and maritime terrorism. International efforts have made strides in reducing piracy, but maritime security remains a concern, requiring sustained efforts to combat illicit activities and safeguard commerce.
3.3 Role in Regional Stability
Somalia plays a crucial role in fostering regional stability and security in the Horn of Africa. As a member of IGAD, Somalia engages in regional initiatives addressing common challenges, including conflict resolution and economic integration. Its interactions with neighboring countries influence regional dynamics.
4. The Free and Open Indo-Pacific: Implications for Somalia
4.1 Understanding the FOIP Concept
The FOIP seeks to promote stability, prosperity, and cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, emphasizing a rules-based order, freedom of navigation, and open markets. Inclusivity, transparency, and respect for international law are central to the FOIP's efforts to foster regional development and cooperation.
4.2 Opportunities for Somalia
Within the FOIP framework, Somalia can benefit from economic development, maritime security, and governance reform. For example, the emphasis on economic connectivity aligns with Somalia's aspirations for regional integration and growth, while enhanced maritime security cooperation can address piracy and illegal fishing.
4.3 Challenges and Constraints
Somalia faces challenges in fully embracing the FOIP, including security concerns, governance deficiencies, and capacity constraints. Persistent threats from groups like Al-Shabaab, governance deficits, and limited institutional capacity hinder Somalia's ability to realize the benefits of the FOIP fully.
Navigating the complex geopolitical dynamics and power competition in the region is a key emerging challenge for Somalia and most East African countries in the context of the Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) initiative, particularly between major players such as China and the United States. As Somalia seeks to strengthen its ties with FOIP-aligned countries to promote stability and economic development, it must also balance its relationships with other influential actors, including China. China has been expanding its presence in Africa, including Somalia, through investments in infrastructure projects, trade agreements, and diplomatic engagements. While these investments can offer valuable resources and opportunities for Somalia's development, they raise concerns about debt sustainability, transparency, and potential geopolitical dependencies.
Internal challenges, such as political instability, terrorism, and governance issues, can undermine the ability to fully leverage the opportunities presented by the FOIP initiative. Addressing these challenges is essential for Somalia and other East African countries to enhance their credibility as reliable partners in regional efforts to promote peace, security, and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific.
The Israel-Palestine conflict presents multifaceted challenges to the Free and Open Indo-Pacific initiative, ranging from regional instability and maritime security concerns to diplomatic tensions and humanitarian crises. Addressing the root causes of the conflict and promoting peaceful resolution through dialogue, negotiation, and diplomacy is essential to advancing the goals of a free, open, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region.
The conflict between Russia and Ukraine presents multifaceted challenges to the Free and Open Indo-Pacific initiative, spanning geopolitical tensions, energy security, economic impacts, security concerns, and diplomatic challenges. Addressing the root causes of the conflict and promoting peaceful resolution through dialogue and diplomacy is essential to advancing the goals of a free, open, and prosperous Indo-Pacific region.
5. The Free and Open Indo-Pacific: Implications for Somalia
Understanding the FOIP Concept: The FOIP seeks to promote stability, prosperity, and cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, emphasizing a rules-based order, freedom of navigation, and open markets. Inclusivity, transparency, and respect for international law are central to the FOIP's efforts to foster regional development and cooperation.
Within the FOIP framework, Somalia can benefit from economic development, maritime security, and governance reform. For example, the emphasis on economic connectivity aligns with Somalia's aspirations for regional integration and growth, while enhanced maritime security cooperation can address piracy and illegal fishing.
Somalia faces challenges in fully embracing the FOIP, including security concerns, governance deficiencies, and capacity constraints. Persistent threats from groups like Al-Shabaab, governance deficits, and limited institutional capacity hinder Somalia's ability to realize the benefits of the FOIP fully.
Despite challenges, Somalia can leverage the FOIP as a catalyst for peace and conflict resolution in the Horn of Africa. By engaging with partners within the FOIP framework, Somalia can access resources and expertise to address security challenges. Additionally, dialogue, cooperation, and inclusive development initiatives can foster reconciliation and build social cohesion.
Examining experiences from regional actors like Japan and international support from organizations like the UN can provide valuable insights into effective approaches to peace-building and conflict resolution in Somalia. Success stories and challenges within Somalia, including experiences from Somaliland and Puntland, offer lessons in governance, resilience, and community engagement.
6. Pathways to Peace and Conflict Resolution
Despite challenges, Somalia can leverage the FOIP as a catalyst for peace and conflict resolution in the Horn of Africa. By engaging with partners within the FOIP framework, Somalia can access resources and expertise to address security challenges. Additionally, dialogue, cooperation, and inclusive development initiatives can foster reconciliation and build social cohesion.
To strengthen the goals and objectives of the Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) initiative in Eastern African countries, the following recommendations should be considered:
Enhance Maritime Security Cooperation: Eastern African countries should prioritize enhancing maritime security cooperation to combat piracy, illegal fishing, and other maritime crimes. This could involve joint patrols, information-sharing mechanisms, capacity-sharing mechanisms, capacity-building initiatives, and the establishment of regional maritime security frameworks to safeguard maritime trade routes and promote freedom of navigation in the Indian Ocean.
Foster Economic Connectivity: Eastern African countries can strengthen economic connectivity by investing in critical infrastructure projects such as ports, roads, and railways to improve trade links within the region and with other Indo-Pacific partners. Facilitating trade facilitation measures, reducing trade barriers, and promoting regional economic integration through platforms like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) can also enhance economic cooperation and prosperity.
Promote Sustainable Development: Sustainable development initiatives focused on sectors such as agriculture, tourism, and renewable energy can contribute to poverty alleviation, job creation, and environmental conservation in Eastern African countries. By promoting sustainable development practices and green technologies, countries can address socio-economic challenges while contributing to the long-term resilience and prosperity of the region.
Strengthen Regional Cooperation Mechanisms: Eastern African countries should prioritize strengthening existing regional cooperation mechanisms, such as the Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD) and the East African Community (EAC), to address shared security, economic, and development challenges. Enhancing coordination on peacebuilding, conflict resolution, and disaster management can foster greater regional stability and cooperation.
Promote People-to-People Exchanges: Encouraging people-to-people exchanges, cultural diplomacy, and educational partnerships can promote mutual understanding, tolerance, and cooperation among Eastern African countries and other Indo-Pacific partners. Initiatives such as student exchange programs, cultural festivals, and academic collaborations can help build bridges between communities and strengthen ties between countries in the region.
Engage with External Partners: Eastern African countries should actively engage with external partners, including countries in the Indo-Pacific region, international organizations, and multilateral institutions, to leverage expertise, resources, and support for advancing FOIP goals and objectives. Building strategic partnerships based on mutual interests and shared values can enhance regional security, prosperity, and stability.
Key recommendation to strengthen the goals and objectives of FOIP to developed countries like Japan, India, USA, and others:
To strengthen the goals and objectives of the Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) initiative for developed countries like Japan, India, the USA, and others, the following key recommendations could be considered:
Strategic Alignment and Coordination: Developed countries should prioritize strategic alignment and coordination among FOIP partners to ensure coherence and effectiveness in pursuing shared goals and objectives. This could involve regular consultations, joint planning exercises, and the establishment of coordinating mechanisms to enhance cooperation on security, economic, and diplomatic initiatives in the Indo-Pacific region.
Maritime Security Cooperation: Given the strategic importance of maritime security in the Indo-Pacific, developed countries should deepen cooperation on maritime security initiatives, including joint patrols, information sharing, capacity building, and promoting maritime domain awareness. Strengthening naval capabilities, supporting coast guard operations, and combating piracy, illegal fishing, and maritime trafficking are key areas for collaboration.
Economic Connectivity and Infrastructure Development: Developed countries can support economic connectivity and infrastructure development in the Indo-Pacific by investing in critical infrastructure projects such as ports, roads, railways, and energy networks. Enhancing connectivity will facilitate trade, investment, and regional integration while promoting sustainable development and resilience to external shocks.
Trade and Investment Partnerships: Developed countries should prioritize trade and investment partnerships with Indo-Pacific countries to foster economic growth, innovation, and prosperity. This could involve negotiating free trade agreements, promoting investment flows, and supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to participate in global value chains. Strengthening economic ties will create opportunities for job creation, technology transfer, and inclusive development.
Support for Rule of Law and Good Governance: Upholding the rule of law, good governance, and respect for human rights are essential for maintaining a free, open, and inclusive Indo-Pacific region. Developed countries should support capacity-building initiatives, legal reforms, and institution-building efforts to strengthen democratic institutions, promote transparency, and combat corruption. Strengthening governance will contribute to stability, confidence, and long-term sustainability in the region.
Innovation and Technology Cooperation: Leveraging innovation and technology cooperation can drive economic growth, enhance competitiveness, and address shared challenges in areas such as cyber security, climate change, and public health. Developed countries should support research and development collaboration, technology transfer, and digital infrastructure projects to harness the transformative power of innovation for the benefit of all Indo-Pacific countries.
7. Case Studies and Best Practices
Examining experiences from regional actors like Japan and international support from organizations like the UN can provide valuable insights into effective approaches to peacebuilding and conflict resolution in Somalia. Success stories and challenges from within Somalia, including experiences from Somaliland and Puntland, offer lessons in governance, resilience, and community engagement.
8. Concluding remarks
Somalia's perspective on the Free and Open Indo-Pacific underscores the opportunities and challenges inherent in the region's geopolitical landscape. By actively engaging within the FOIP framework, Somalia can advance its interests while contributing to broader objectives of peace and stability in the Horn of Africa.
The Free and Open Indo-Pacific (FOIP) initiative represents a comprehensive and inclusive approach to promoting peace, stability, prosperity, and cooperation across the vast Indo-Pacific region. By emphasizing the principles of freedom, openness, inclusivity, and respect for international law, FOIP countries seek to build a regional order conducive to mutual respect, shared prosperity, and sustainable development.
Through strategic alignment, coordination, and cooperation, FOIP countries aim to address common challenges such as maritime security threats, economic disparities, and geopolitical tensions while capitalizing on the immense opportunities for trade, investment, and innovation the Indo-Pacific region offers. By fostering economic connectivity, supporting infrastructure development, promoting good governance, and investing in people-to-people exchanges, FOIP countries can build a more resilient, dynamic, and interconnected Indo-Pacific community.
As the FOIP initiative continues to evolve and expand, countries must reaffirm their commitment to the principles and values that underpin it while remaining flexible and adaptive to changing regional dynamics and emerging challenges. By working together in a spirit of cooperation, dialogue, and mutual respect, FOIP countries can realize the vision of a Free and Open Indo-Pacific that benefits the region's inhabitants and the broader global community.
(The author is a Advisor to the Ministry of Interior, Federal Affairs & Reconciliation )
References:
Government of Japan. “New Plan for a Free and Open Indo-Pacific: Policy Speech by PM Kishida.” Last modified May 2023. https://www.japan.go.jp/kizuna/2023/05/new_plan_for_free_and_open_indo-pacific.html.
Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. “Foreign Policy: Free and Open Indo-Pacific.” Last modified April 2023. https://www.mofa.go.jp/policy/page25e_000278.html.
Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo. “ROLES 7th International Conference on Emerging Technologies and the Future of Work.” Accessed online: https://roles.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp/event/20240227en.
同じカテゴリの刊行物
コメンタリー
2026.01.27 (火)
